USB applications: Questions and answers
Questions
- How do I install a program that does not come with an installer?
- How can I launch USB apps?
- And how do I launch and use no-install apps on my PC?
- How about portable apps that only come with an installer?
- How do I uninstall a program I installed manually?
- What is an argument? How do I use an argument?
- What makes a Windows application portable?
- I deleted a file from my keydrive and it’s not in the recycle bin!
- Some apps take too long to close. Is there something wrong?
- Can I just insert the keydrive and have some apps start automatically?
- Will I be able to use my keydrive in any (Windows) computer?
- Are keydrives reliable? What if my keydrive fails and I lose all my files?
- What if my keydrive is lost or stolen? How can I secure my private data?
- I want to make my Windows portable and run it from a keydrive!
Answers
- How do I install a program that does not come with an installer?
-
To install a program that does not come with an installer, you need to do manually the most basic thing installers do:
Make a directory for the program, say IrfanView for IrfanView, and unpack the contents of the archive there.
This directory can be anywhere. However, to keep your keydrive nicely organized, it’s better to have a directory where you put all your program directories, something like X:\Apps or X:\Programs.
In the example below, we use 7-Zip to “install” the file manager A43 in the A43 directory within >Apps. The drive letter of the keydrive in this example is L, but it can be any letter not already in use for another drive.
- Right-click on the ZIP file
- Select 7-Zip / Extract files…
- Click the … button to select the keydrive letter and the directory of your programs
- Type a backslash and the name of the directory you want to unpack A43 to: \A43
- Click OK. 7-Zip will create a directory A43 in L:\Apps, and unpack the contents there
- The file to start the program is L:\Apps\A43\A43.exe
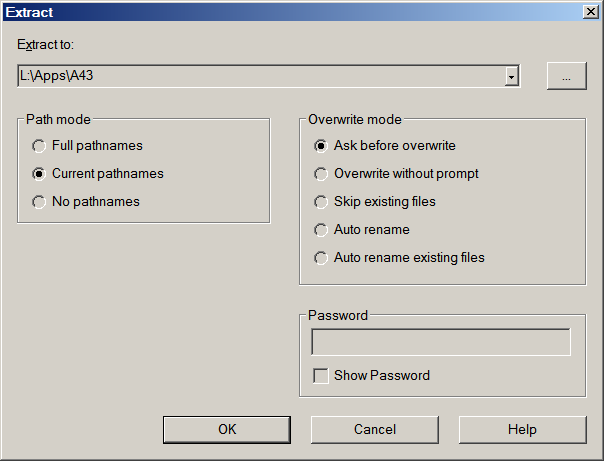
The process is similar with any archiver and has many variations. For example, you can use Windows Explorer to browse to the Apps directory, open it, right-click on an empty space, select New, Folder, make a folder named A43, then open the ZIP archive in 7-Zip, select all contents, and drag them to the new folder.
- How do I launch USB apps?
-
You simply run the program’s executable. E.g., go to the KeePass directory and double-click on KeePass.exe (if extensions are not visible, the file you need is recognizable by its icon, usually the app logo).
For convenience, you can make batch files for your USB apps, or one batch file for all apps you use regularly. For more convenience, use an app launcher like PStart. If you prefer using keyboard shortcuts, you can make launchers with AutoHotkey.
- And how do I launch and use no-install apps on my PC?
-
Unpack the program to a directory in Program Files, go to the directory and double-clicke the program’s executable file. Open the program’s settings and look for options to add a shortcut to the desktop, an item to the start menu, etc. Some programs also offer an option to add an item to the context menu (the menu that pops up when you right-click somewhere, and whose items are always relevant to the context).
If there are no such options, right-click on the executable and send a shortcut icon to the desktop. Once the shortcut is on the desktop, you can copy it to the start menu or to the quick launch bar (or to the startup folder in the start menu, if you want the program to start automatically with Windows).
- How about portable apps that only come with an installer?
-
Install normally, go to C:\Program Files and copy the program’s directory to the keydrive.
E.g., for IrfanView copy C:\Program Files\IrfanView to the Apps directory in the keydrive, so that the directory of the portable IrfanView is X:\Apps\IrfanView — The program directory in Program Files may contain uninstallation files like install.log, unins000.exe, uninstall.exe, etc. You can delete these from the keydrive, to save space. If you only needed the program for portable use, you can then uninstall it from your computer.
Some portable programs, e.g. KeePass, offer two download options: A ZIP archive with just the program files, and an installer. If you want to use the program both on your PC and on the go, get the installer. It will install the program in your PC with desktop shortcuts, menu items and everything. Then, you can copy its directory to the keydrive.
- How do I uninstall a program I installed manually?
-
Delete its folder from the keydrive.
- What is an argument? How do I use an argument?
-
Arguments (also called command line options, switches, or parameters) are instructions that tell a program to change its default behaviour. The arguments a program supports are usually listed in its help file.
Some programs support arguments that tell them to behave like a portable program. For example,
--no-plugins-cacheand--config="vlcrc"are two arguments that tell VLC media player not to create a plugins cache in Documents and Settings, and to read its settings from the vlcrc file in the program’s directory (or make the vlcrc file if it doesn’t exist).To use arguments in a batch file or in an AutoHotkey command, add them after the program path. If you use PStart, just put them in the special box. Below are two examples for starting Skype and VLC through PStart.
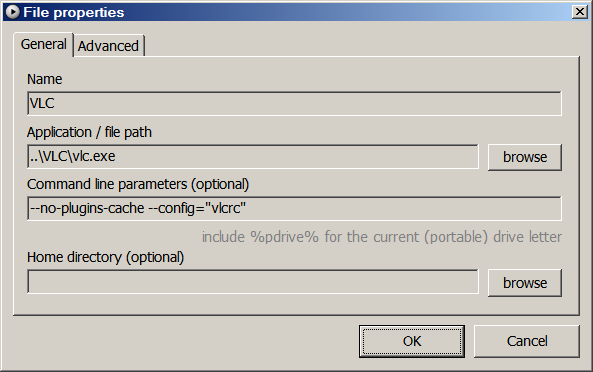
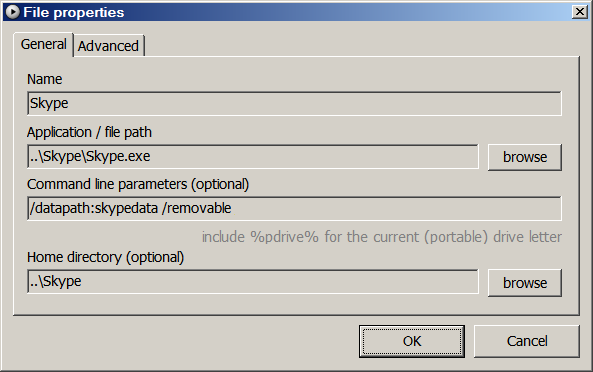
- What makes a Windows application portable?
-
- It must not depend on (or place) files outside its directory, except for common system files
-
It must keep its settings in its directory, and not in the registry (or in Documents and Settings),
because:
- If it stores settings in the Windows registry or in the user profile, its settings are not portable; and
- Even if it writes unnecessary information there, it is not good to mess in this way with a public computer or with another person’s computer
In other words, the program must be able to store in its own directory all files it generates and on which it depends (with the exception of common system files present in all Windows systems).
- I deleted a file from my keydrive and it’s not in the recycle bin!
-
Files deleted from flash drives do not go into the recycle bin. However, if the file has not been overwritten by another file or files, it is still in the keydrive. You may be able to recover it with a program like Restoration or PC Inspector File Recovery. File Recovery has to be run from a different drive/partition. Restoration can be run from anywhere:
- Minimize all keydrive activity, that is, do not open/close/copy/move any other programs/files
- Run Restoration or File Recovery
- Restore to a different drive, especially if you want to restore multiple files
- Some apps take too long to close. Is there something wrong?
-
Just wait! Transfer rates between USB flash drives and a computer are relatively slow. Sometimes, exit time is prolonged by the way a program updates its settings upon exiting.
- Can I just insert the keydrive and have some apps start automatically?
-
Not easily. Microsoft says: “The Autorun capabilities are restricted to CD-ROM drives and fixed disk drives. If you need to make a USB storage device perform Autorun, the device must not be marked as a removable media device and the device must contain an Autorun.inf file and a startup application.” — Source: USB Storage - FAQ for Driver and Hardware Developers (Wayback Machine)
A keydrive that claims to support autorun: www.udrw.com.
- Can I use my keydrive in any (Windows) computer?
-
Yes. Windows ME, 2000, XP, and 2003 support USB drives natively. Windows 98 needs extra drivers. These come with the keydrive, or are available at the manufacturer’s site. You can also use the keydrive in other modern operating systems, but only to transfer files, not to run Windows programs.
- Are keydrives reliable? What if my keydrive fails and I lose all my files?
-
Physically, yes, they are. You can even wash them in a wash machine. However, flash drives sustain a limited number of read/write operations. See: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USB_flash_drive.
- What if my keydrive is lost or stolen? How can I secure my private data?
-
Some keydrives come with security software. We haven’t tried any such software. A solution some use is TrueCrypt in “traveller mode”, i.e., portable mode: It allows you to make an encrypted container in the keydrive and drop everything in it. TrueCrypt is open-source, which is good for encryption software. However, it suffers from a couple of limitations for portable use.
- I want to make my Windows portable and run it from a keydrive!
-
This is not possible. However, you can use Bart Preinstalled Environment to make a Windows CD that will boot into a Win32 environment with a basic GUI. It is useful mainly for administrative tasks, rescue operations etc. Other operating systems are more suited to portable use. See:
- Damn Small Linux: www.damnsmalllinux.org
- Feather Linux: berlios.de/software/feather-linux/
- Puppy Linux: puppylinux-woof-ce.github.io
- The various Howtos at LiveDistro: LiveDistro on the Wayback Machine
Changelog
2025-08
- Updated links to use HTTPS.
- Changed the Microsoft USB Storage link to a Wayback Machine link.
- Changed en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keydrive to en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USB_flash_drive.
- Changed featherlinux.berlios.de to www.berlios.de/software/feather-linux.
- Changed www.goosee.com/puppy to puppylinux-woof-ce.github.io.
- Changed LiveDistro link to a Wayback Machine link.